Discover the world of woven fabric, distinguishing it from knitted fabric, exploring its structure, uses, and the benefits it offers. Fashion Bandung awaits you.
Learn about woven fabrics
What is woven fabric?

What is woven fabric?
Woven fabric, also known as a woven textile, is a type of fabric that is produced by the interlacing of warp and weft threads on a frame. This frame can be either a manually operated loom or a machine-operated loom used in industrial manufacturing processes. The weaving process involves the careful interlacing of vertical warp threads with horizontal weft threads to create a tight, durable, and cohesive fabric structure.
Woven fabric is constructed through a manufacturing process that involves the intricate interweaving of two sets of yarns known as the warp and weft. These yarns are combined in such a way that they form a network structure, resulting in the creation of woven fabric.
The process of manufacturing woven fabrics begins with the selection of fibers. These fibers can come from various sources, such as natural materials like cotton, silk, or wool, as well as synthetic materials like polyester or nylon.
Once the desired fibers have been chosen, they are carefully spun into yarns. The warp yarns are stretched lengthwise on a loom, forming a strong and sturdy foundation for the fabric. The weft yarns, on the other hand, are woven horizontally through the warp yarns, creating a crisscross pattern. The tension of the loom ensures that the yarns intertwine securely, resulting in a stable fabric structure.
The weaving process involves a series of intertwining the warp and weft yarns, which are interlaced through a set of mechanized or computerized movements. These movements allow the warp and weft threads to pass over and under each other, ultimately forming a cohesive fabric. The complexity of the weaving pattern can vary, resulting in different types of weaves, such as plain, twill, or satin.
During this manufacturing process, the yarns may undergo additional treatments, such as dyeing or finishing, to enhance their aesthetic appeal, durability, or other desired properties.
Overall, the construction of woven fabric is a precise and intricate process that entails the combination of warp and weft yarns through weaving, resulting in a versatile and durable textile that can be used for various applications.
The weaving process of making woven fabric involves interlacing two sets of yarn, the warp and weft, to create a stable and durable material. This process typically includes multiple steps, starting with preparing the warp and weft yarns.
To prepare the warp yarn, it is typically wound onto a beam or a large spool. The number of warp yarns and their arrangement depends on the desired fabric structure and pattern. The warp yarns are then threaded through the loom, which is a machine specifically designed for weaving.
The weft yarn, on the other hand, is wound onto a separate spool called a weft bobbin. This bobbin is placed in a shuttle or other weft insertion mechanism.
Once the warp and weft yarns are prepared, the weaving process can begin. The weaver operates the loom and controls the motion of the warp and weft yarns. The warp yarns are lifted or lowered in a specific sequence, known as the shedding motion, to create an open space, also called a shed.
The weft yarn is then inserted into the shed using the shuttle or any other suitable method. The weft yarn is passed through the shed from one side of the loom to the other.
After the weft yarn is inserted, the warp yarns are pressed together tightly to lock the weft in place. This action is known as beating-up.
The entire process of shedding, inserting the weft, and beating-up is repeated continuously until the desired fabric length is reached.
Once the weaving process is complete, the fabric is typically removed from the loom and undergoes various finishing processes, such as washing, dyeing, and pressing, to enhance its appearance, texture, and durability.
Overall, the weaving process is a meticulous and precise technique that requires skill and attention to detail to create high-quality woven fabrics with diverse patterns, textures, and uses.
Furthermore, it is worth considering the option of blending various types of fibers in specific ratios. For instance, one can opt for a combination of 80% natural fibers and 20% synthetic fibers. This blend offers several advantages for woven fabrics, including enhanced resilience and flexibility. In contrast to knitted fabrics, woven fabrics do not exhibit significant elasticity. The weaving process for woven fabrics involves employing techniques like plain weave, satin weave, or twill weave, each contributing distinct and varied characteristics to the final product.
See more:
Weaving styles

Weaving patterns are a common feature in our daily lives. These intricate patterns are utilized in various aspects of everyday life and are often found in textiles and fabrics used for clothing, household items, and accessories. From traditional cultural garments to modern fashion trends, weaving patterns add a touch of artistic intricacy to our everyday attire. They can also be seen in decorative items such as rugs, tapestries, and upholstery fabrics, where they bring a sense of warmth and aesthetic appeal to our living spaces. Whether consciously or subconsciously, we encounter these weaving patterns regularly, appreciating their beauty and the skill required to create them.
In our daily lives, we come across a wide variety of woven fabrics that serve different purposes. These fabrics are created through the process of intertwining threads or yarns to form a cohesive and durable material. Here are some commonly encountered types of woven fabrics:
1. Cotton: This natural fabric is derived from the cotton plant and is known for its soft and breathable nature. It is used extensively in making clothing, bedsheets, towels, and many other household items.
2. Silk: Silk is a luxurious and lustrous fabric produced by silkworms. It is highly sought after for its smooth texture and elegant appearance. Silk is commonly used to create high-end garments, scarves, and home decor items.
3. Linen: Derived from the flax plant, linen is a lightweight and breathable fabric that is ideal for warm weather. It is known for its crisp texture and natural sheen. Linen is commonly used for making clothing, tablecloths, and curtains.
4. Wool: Wool is a natural fiber obtained from animals like sheep, goats, and alpacas. It is well-known for its excellent insulation properties, making it ideal for cold weather garments. Wool is also used to create blankets, rugs, and upholstery fabrics.
5. Polyester: Polyester is a synthetic fabric that offers durability and resilience. It is known for its resistance to wrinkles, shrinkage, and fading. Polyester fabrics are commonly used in making sportswear, swimwear, and various everyday garments.
6. Denim: Denim fabric is a sturdy and durable cotton twill material primarily used in the production of jeans. It is recognized for its characteristic diagonal ribbing, known as twill weave, and is a popular choice for casual clothing.
7. Velvet: Velvet is a plush and luxurious fabric that features a dense pile. It is made by weaving two sets of yarns using a special technique that creates a soft and smooth surface. Velvet is often used for creating formal attire, upholstery, and decorative accessories.
8. Satin: Satin fabric is known for its glossy and smooth texture. It is produced using a weaving technique known as the satin weave, which imparts a lustrous appearance. Satin is commonly used for making evening gowns, lingerie, and accessories.
9. Corduroy: Corduroy fabric is characterized by its distinct ribbed texture, often referred to as “wales.” It is created by weaving extra sets of fiber along with the base fabric. Corduroy is commonly used for making trousers, jackets, and upholstery.
10. Tweed: Tweed is a rough and durable fabric that is usually made from wool. It is known for its unique texture and traditional, rustic appearance. Tweed fabric is commonly used for creating jackets, skirts, and accessories, especially in colder climates.
- Poplin Fabric: Poplin weave fabrics are similar to plain weave fabrics, but differ in that the warp yarns are usually twice as many as the weft yarns and the warp yarns are smaller in size than the weft yarns, creating a fabric surface that feels durable and smooth.
- Herringbone woven fabric: The thread forms a V-shape on the surface, often using wool and has many colors with a variety of colors, creating interior products such as upholstery or sofas.
- Twill fabric: The yarns lie diagonally, reducing wrinkles and keeping their shape better. The twill weave involves weaving the weft yarns over the warp yarns, creating a unique diagonal texture. The right and wrong sides are clearly visible, with a very distinctive diagonal line.
- Satin weave fabric: Complex weave, high gloss, often used for interior decoration. Often used for fabrics with outstanding colors. Shiny and smooth, creating highlights.
- Plain weave fabric: The simplest type of woven fabric, with each weft thread always lying under a warp thread, forming a 90 degree angle. The surface is uniform, traditional and suitable for sewing a variety of fashion products.
Woven fabrics possess attributes such as durability, strength, breathability, and the ability to hold shape due to their interlaced yarns.

Woven fabric is an excellent choice as it offers a range of appealing qualities including exceptional elasticity, robust strength, and impressive long-lasting durability.
Understanding the structural characteristics of woven fabrics is crucial in assessing their quality and suitability for specific applications. By examining the following details, you will be able to identify and differentiate various types of woven fabrics:
1. Weave: Woven fabrics are created through the interlacing of warp and weft yarns. The weave refers to the specific pattern or manner in which these yarns intersect. Common types of weaves include plain, twill, and satin weaves, each offering distinct properties and appearances.
2. Warp and Weft: The warp yarns run lengthwise in a fabric, while the weft yarns run horizontally, crossing over and under the warp threads. The density and tightness of these yarns greatly affect the strength and drape of woven fabrics.
3. Weight: The weight of a woven fabric refers to the mass per unit area. It can range from lightweight fabrics suitable for delicate garments to heavy-duty fabrics used in industrial applications. The weight of a fabric can influence its ability to provide warmth, breathability, and durability.
4. Thread Count: Thread count indicates the number of warp and weft yarns per square inch of fabric. Higher thread counts generally result in finer, smoother fabrics. This characteristic is often associated with luxury and comfort in bedding and apparel.
5. Strength and Durability: Woven fabrics are renowned for their strength and durability. Factors that contribute to the fabric’s resilience include the quality of fibers, yarns, and the tightness of the interlacing weave. Fabrics with superior strength are suitable for upholstery, heavy-duty apparel, and industrial purposes.
6. Texture: The texture of woven fabrics is determined by the combination of yarn types, weave structure, and finishing processes. Textures can range from smooth to rough, creating visual and tactile differentiation. This characteristic is important for textile design and aesthetic appeal.
7. Breathability: Woven fabrics are typically breathable, meaning they allow air circulation and moisture vapor transmission. This property makes them comfortable to wear, particularly in warm climates or during physical activities. The breathability of a fabric is determined by the density and structure of the weave, as well as the type of fiber used.
8. Printability and Dyeability: Woven fabrics provide a stable base for printing and dyeing processes. The flat, uniform surface allows for precise and vibrant print designs or even dye absorption. This characteristic enhances the versatility and creative possibilities of woven fabrics.
By considering these detailed structural characteristics, you will be able to assess the quality, functionality, and potential uses of various woven fabrics, enabling you to make informed decisions in selecting the right fabric for your specific needs.
- Tight surface: With tight knitting, the surface of the fabric is always tight without looseness, creating a solid and beautiful feeling.
- The weft is perpendicular to the warp: This is an important feature, which helps to define the weave structure and ensure uniformity in strength and elasticity.
- Stretchability: With woven fabric construction the stretchability of woven fabrics can be improved through the addition of spandex, creating flexibility, with a tendency to stretch more lengthwise than crosswise.
- No thread loss and no curling of edges: Woven fabrics are often durable, do not easily lose thread or curl edges after use, keeping the product in its original shape and seams.
- Wrinkle resistance: When using natural fibers, woven fabrics are more wrinkle resistant, keeping the fabric surface looking neat and wrinkle-free.
- Variety of designs and colors: With diverse production processes, woven fabrics are available in many different designs and color gamuts, allowing for creativity and color selection to suit individual needs and preferences.
The raw materials employed in the production of woven fabrics.

Woven fabrics are composed of various materials that are intertwined together to form a cohesive textile. These materials can include natural fibers such as cotton, linen, silk, and wool, as well as synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic. The choice of materials depends on the desired characteristics and properties of the fabric, such as its strength, durability, texture, and appearance. Each material brings its unique qualities to the fabric, contributing to factors such as breathability, moisture-wicking, and resistance to wrinkles or abrasion. The combination of these materials in the weaving process creates a versatile and diverse range of woven fabrics that can be found in countless applications, from clothing and upholstery to household textiles and industrial use.
Woven fabrics are versatile and can be created using a wide range of raw materials. The choice of raw materials for weaving is not restricted by any specific regulations. For instance, when manufacturing cotton or khaki fabrics, the primary raw material utilized is cotton yarn. Conversely, polyester fabrics rely on polyester man-made fibers as the main raw material during the weaving process.
Currently, there are no specific regulations governing the selection of materials for weaving woven fabrics. The choice of materials largely depends on the specific type of fabric the manufacturer intends to produce. Broadly speaking, materials for weaving fabrics can be divided into two main categories: natural fibers and man-made fibers.
- Natural fibers: Includes naturally occurring fibers such as cotton, silk, rayon, and other fibers found in nature. These fibers often provide a breathable and soft feel to woven fabrics.
- Synthetic fibers: A chemically produced fiber made primarily from petroleum. A typical example is polyester, a popular man-made fiber for woven fabrics that is strong, lightweight, and quick-drying.
The choice of material to use in tailoring depends on the specific qualities that the tailor wishes to achieve. These qualities can include factors such as elasticity, durability, and overall feel. Fortunately, there is a wide variety of materials available for tailors to choose from, allowing them to create woven fabrics that cater to a diverse range of applications and individual preferences. This extensive selection ensures that tailors can select the most suitable material that aligns with their desired outcome and meets the specific needs of their customers.
Commonly used woven fabric types today include cotton, polyester, silk, linen, and denim among others.

Various kinds of woven fabrics are commonly utilized in different industries and for various purposes. These fabrics are created by interlacing two or more sets of yarns at right angles to form a stable structure. The types of woven fabrics used can vary greatly in terms of their composition, weight, texture, and strength, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Some examples of woven fabrics that are frequently employed include cotton, silk, linen, wool, polyester, nylon, and denim. These materials offer diverse properties such as breathability, durability, elasticity, moisture-wicking, and heat resistance, among others, making them suitable for applications in clothing, home textiles, furniture upholstery, automotive interiors, industrial equipment, and many other fields. The choice of woven fabric depends on the specific requirements and desired characteristics for each particular application.
Currently, there is a wide range of textiles that are commonly utilized in various industries. These textiles are carefully manufactured to cater to different needs and serve a multitude of purposes. Here are some of the most commonly utilized types of textiles that are prevalent in today’s world:
1. Cotton: Known for its softness and versatility, cotton is one of the most popular textiles worldwide. It is widely used in the production of clothing, home furnishings, and various other products. Cotton fabrics are breathable and absorbent, making them ideal for hot and humid climates.
2. Synthetic fibers: These are man-made fibers such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic. Synthetic fibers are prized for their durability, wrinkle resistance, and resistance to fading. They are extensively used in the production of clothing, sportswear, carpets, and upholstery.
3. Silk: Recognized for its lustrous appearance and luxurious feel, silk has been a prized textile for centuries. Derived from the fibers of silkworm cocoons, it is an excellent choice for high-end clothing, bedding, and luxurious home furnishings.
4. Wool: Derived from animal hair, primarily sheep, wool is widely used for its exceptional warmth and insulation properties. It is often used in the production of winter clothing, blankets, and carpets. Wool is also known for its ability to regulate body temperature and wick away moisture.
5. Linen: Made from flax fibers, linen is a versatile and durable textile. It is highly breathable, making it suitable for warm climates. Linen is commonly used in the production of beddings, clothing, and home furnishings.
6. Velvet: This luxurious and plush fabric is typically made from silk, cotton, or synthetic fibers. Characterized by its softness and unique texture, velvet is often used in the production of high-end clothing, upholstery, and decorative items.
7. Denim: A sturdy cotton fabric woven in a diagonal pattern, denim is highly durable and commonly associated with jeans. It is known for its versatility, making it suitable for various garments and home decor items.
8. Polyester blends: These are textiles that combine polyester with other fibers such as cotton or wool. Polyester blends offer the best of both worlds, combining the durability and wrinkle resistance of polyester with the breathability and natural feel of other fibers.
These are just a few examples of the wide array of textiles used today. Each textile offers unique properties and characteristics, allowing for a diverse range of options for manufacturers, designers, and consumers across numerous industries.
- Khaki: Khaki fabric is a popular woven fabric, usually made from cotton or a combination of different fibers. It is durable and widely used in the garment industry and in the production of accessories such as bags, backpacks, shoes, etc.
- Taffeta fabric: Taffeta fabric has good gloss and light-catching ability, woven with fine ribs on the surface. Usually made from silk or combined with many types of synthetic fibers, Taffeta fabric is often used to make dresses.
- Voile Fabric: Voile fabric is soft, light, and drapes. It is transparent and is made from many types of fibers such as rayon and polyester. Voile fabric is widely used in the garment and interior decoration industries.
- Velvet: Velvet fabric is woven with the main ingredient being silk, then replaced by artificial fibers. Smooth and soft, used to produce many unique products.
- Denim Fabric: Denim is a woven cotton fabric, commonly used for jackets, trousers and workwear.
- Draper: Felt fabric is made in plain or twill weave, has a thick, soft structure, and is mainly used to make clothes to keep the body warm.
- Kashmir Silk Fabric: Kashmir silk fabric is plain woven, has many surface patterns, and is often used to make dresses, shawls and floral shirts.
- Muslin fabric: Muslin is a plain woven fabric, light and thin, suitable for summer. Usually made from cotton, safe for children, and used in making clothes and towels.
- Organza Fabric: Organza is a plain woven fabric, thin and light but stiffer than chiffon and silk. Often used to make clothes such as shirts, dresses, and blouses.
- Cotton: Cotton fabrics have many different weaves, can be plain weave, twill weave. The combination with other fibers such as polyester, spandex helps to improve the durability and elasticity of cotton fabrics.
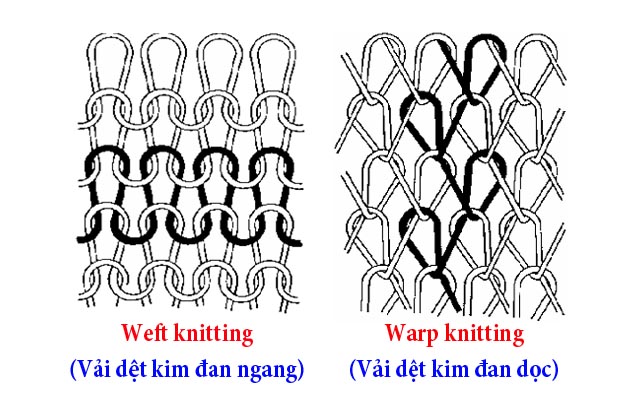
How can one differentiate between fabrics made through weaving and fabrics made through knitting?
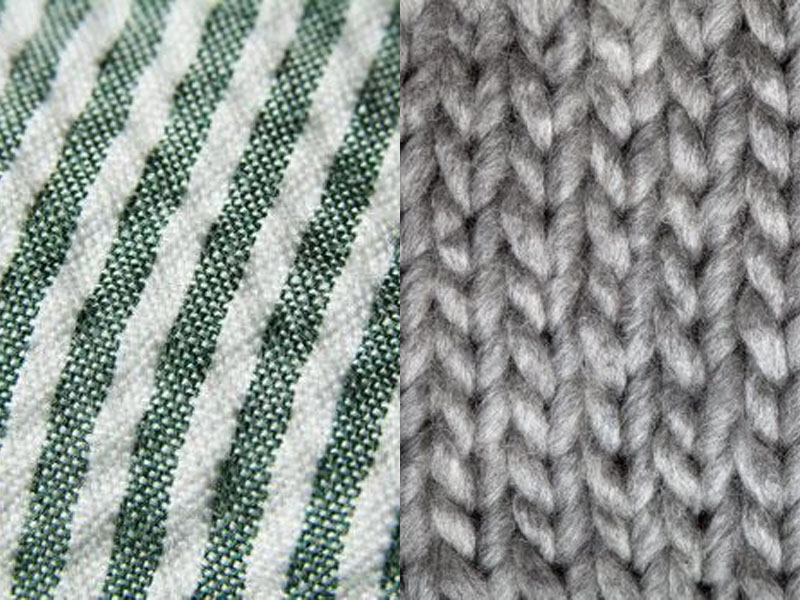

Woven and knitted fabrics are types of textile constructions that differ in their production process, resulting in distinct characteristics and properties.
Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two sets of yarns, known as the warp and weft, perpendicular to each other. This weaving process involves the use of a loom, where the warp yarns are stretched vertically, while the weft yarns are interwoven horizontally. As a result, woven fabrics exhibit a strong and stable structure, with little stretchability. This construction method enables a variety of weaving patterns, such as plain, twill, and satin weaves, which contribute to the fabric’s texture and appearance. Woven fabrics are generally known for their durability, abrasion resistance, and resistance to fraying.
On the other hand, knitted fabrics are formed by interlooping yarns to create a series of interconnected loops. This process can be achieved manually with knitting needles or mechanically through knitting machines. Knitted fabrics have a characteristic stretchability and elasticity due to the loops’ ability to expand and contract. This construction method allows for greater flexibility and comfort, making knitted fabrics ideal for garments that require mobility, such as activewear and underwear. Moreover, knitted fabrics have good breathability and drape, as the interlocking loops create a more open and airy structure.
In terms of appearance, woven fabrics tend to have a more structured and smooth surface due to the interlacing of yarns. They can exhibit intricate patterns, prints, and designs since the weaving process enables more precise control over the placement of different yarns. On the other hand, knitted fabrics often have a more textured and uneven surface, with a looped, interwoven appearance. This construction method allows for the creation of various stitch patterns and textures, including ribbing, cable knits, and jacquard designs.
In terms of performance, woven fabrics excel in strength, durability, and resistance to tearing. They are often used in upholstery, heavy-duty garments, and home linens. Knitted fabrics, while not as strong as woven fabrics, offer more flexibility and stretchability, making them suitable for garments that require a close fit and unrestricted movement, such as sportswear and swimwear.
Overall, the choice between woven and knitted fabrics depends on the specific requirements of the application, including desired characteristics, performance, and aesthetic preferences. Both fabric constructions have their unique advantages, and understanding their differences allows for informed decisions in selecting the most suitable fabric for a particular purpose.
In order to provide a comprehensive understanding of the differences between woven and knitted fabrics, Fashion Bandung has meticulously compiled a detailed comparison table. This table aims to present you with the most precise and accurate information regarding the unique characteristics, properties, and production processes associated with these two distinct types of fabrics. By referring to this comprehensive resource, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions and acquire a thorough understanding of the qualities that set woven and knitted fabrics apart from each other.
| Properties | Knitted fabric | Woven fabrics |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticity and stretch | Naturally elastic and stretchy | Less elastic, less stretch (unless made from stretch fibers) |
| Thinness | Provides unique slimness | Usually less slender |
| Softness | Soft and stretchy | The fabric is quite stiff and rough. |
| Preservation capacity | Mostly no ironing required | Needs regular ironing due to wrinkling tendency |
| Insulating properties | Has insulating properties | – |
| Maintain wrinkles | Less wrinkles | Prone to wrinkling of clothes |
One way to differentiate fabrics is by carefully examining their grain. The fabric grain refers to the alignment of the threads in the fabric. By observing the fabric grain, you can determine the direction of the threads, which can provide valuable information about the fabric’s characteristics and properties. This involves closely inspecting the threads in the fabric and noticing if they run vertically (lengthwise), horizontally (crosswise), or at an angle (bias). By paying attention to the fabric grain, you can identify the type of weave used, the level of stretchiness or stiffness, and even the potential for pattern matching or draping capabilities.
- Knitted fabric: This yarn is repeated many times to create tiny loops, similar to braiding hair, creating a tightly woven fabric surface with small loops connecting one another.
- Woven fabrics: The warp and weft threads are created and woven over each other, forming a tight structure.
Distinguishing between fabrics can be done by evaluating their stretchability.
- Knitted fabric: When pulled horizontally, it will stretch significantly, when pulled vertically, it can only stretch a little.
- Woven fabrics: Cannot stretch much vertically, only slightly horizontally.
Tips for distinguishing anti-wrinkle fabric from regular fabric:
1. Look for special labeling: Anti-wrinkle fabric often comes with labels or tags that explicitly indicate its wrinkle-resistant properties. Keep an eye out for terms like “wrinkle-free,” “no-iron,” or “crease-resistant.”
2. Examine the fabric texture: Anti-wrinkle fabrics tend to have a smoother texture compared to regular fabrics. Run your hand over the fabric and check if it feels slightly different or has a slightly sheen appearance. This could be an indication of its wrinkle-resistant properties.
3. Observe the fabric drape: Anti-wrinkle fabric usually has better draping qualities than regular fabric. It should fall smoothly and have a more structured appearance when hung or worn. In contrast, regular fabric might have more creases or wrinkles when hanging.
4. Conduct a wrinkle test: Take a small section of the fabric and scrunch it tightly in your hand. Release the fabric and see how quickly the wrinkles disappear. Anti-wrinkle fabric should bounce back and have minimal wrinkles, while regular fabric may retain more creases.
5. Consider the care instructions: Check the care label attached to the fabric. Anti-wrinkle fabric often requires specific care instructions, such as low-heat ironing or no ironing at all. Regular fabric, on the other hand, may have more flexible care requirements.
6. Seek manufacturer’s information: If still uncertain, research the fabric manufacturer online. Look for their product descriptions or specifications, as they often provide information about the specific properties of their fabrics, including anti-wrinkle capabilities.
By utilizing these tips, you will be able to distinguish anti-wrinkle fabric from regular fabric and make an informed decision when purchasing garments or textiles.
- Knitted fabric: When grasped and released, the fabric can flatten again in seconds.
- Woven fabrics: When grasped and released, the fabric tends to retain wrinkles that do not recover immediately without ironing.
Woven fabrics are widely used in various aspects of modern life, including clothing, upholstery, household items, and industrial applications.

Woven fabrics play a significant role in various industries, particularly in the fashion and home furnishings sectors. These fabrics are highly valued for their versatility and numerous applications in creating stylish clothing, as well as functional and aesthetically pleasing items for homes such as curtains, upholstery, and bedding. With their intricate interlacing of vertical and horizontal yarns, woven fabrics offer a wide range of textures, patterns, and strength, making them indispensable in these industries.
Woven fabrics are highly versatile textiles that offer a wide range of applications in both fashion and interior design. These fabrics go beyond being just suitable for everyday clothing, as they can be utilized in various areas of life.
In terms of fashion, woven fabrics can be molded into an array of garments. They are used to create different styles, such as khaki pants, taffeta skirts, and even children’s clothing made from Muslin. The varied texture and structure of woven fabrics allow designers to create unique and aesthetically pleasing outfits for people of all ages.
Moreover, woven fabrics are not limited to fashion alone. They also find extensive use in interior design. These textiles can be tailored to make curtains, upholstery, and decorative textiles for furniture. Their durable nature ensures that woven fabric-based furniture and decorative items have a longer lifespan, making them a practical choice for homeowners and interior designers alike.
The versatility of woven fabrics doesn’t end there. They are also commonly used in various household items such as bed and table linens, towels, and even rugs. The ability of woven fabrics to withstand frequent use and laundering can make them an excellent choice for items that require both functionality and durability.
Overall, woven fabrics offer a plethora of possibilities in both fashion and interior design. Their ability to adapt to different styles and applications makes them an ideal choice for everyday clothing and a range of items used in our daily lives.
Moreover, woven fabrics play a significant role in interior decoration, particularly in the creation of curtains. The diverse range of fabric options, including luxurious velvet, classic linen, and durable polyester, offers homeowners the flexibility to select materials that align with the specific characteristics and style of their individual homes. This versatility not only allows for the revitalization of the living space but also acts as an exquisite accent, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of the room.
Woven fabrics serve as the primary component in the manufacturing of bedding and mattresses. These products are known for their minimal stretching properties, which not only guarantee high quality but also lend an air of luxury to the bedroom ambiance.
Common questions about woven fabrics answered in a concise FAQ format.
What is the meaning of “woven fabric” in English?
- Woven fabric in English can be translated as “woven silk fabric” or “woven fabric”.
What makes woven fabrics unique in their structure?
-
Woven fabrics are made by skillfully intertwining vertical yarns (known as warp) and horizontal yarns (known as weft) in a diagonal manner. This intricate weaving technique forms an intricate web-like structure, giving rise to a fabric that is remarkably soft, seamless, and possesses both durability and elasticity.
-
The unique structure of woven fabrics involves the interweaving of horizontal and vertical threads in a continuous pattern. As a result, the fabric surface features a series of small diagonal or square lines, forming an intricate and textured design. These lines serve to enhance the visual appeal and individuality of woven fabrics, giving them their distinct highlight and character.
-
Woven fabrics, crafted with intricate patterns and meticulous attention to detail, are widely favored in the production of luxurious fashion items, exquisite home furnishings, and various other commodities that require an appreciation for the fabric’s visual allure and superior quality.
summary
The aforementioned article provides a comprehensive answer to the question of what woven fabric is and offers guidance on distinguishing it from knitted fabric. The aim is to provide readers with a detailed understanding of the key features of woven fabrics, ranging from their manufacturing process on a loom to their distinctive properties, including durability, elasticity, and a multitude of design options. By the end of the article, readers will have gained a comprehensive overview of woven fabrics and will be able to differentiate them from other types of fabrics.
Fashion Bandung is a clothing brand that specializes in fashion for men. Located in the city of Bandung, Indonesia, the brand offers a wide range of stylish and trendy clothing options for men of all ages and preferences. From casual wear to formal attire, Fashion Bandung caters to different occasions and personal styles.
The brand takes pride in its carefully curated collection, with a focus on quality materials, impeccable craftsmanship, and attention to detail. Fashion Bandung keeps up with the latest fashion trends and is constantly updating its inventory to offer the most up-to-date styles.
Customers can expect to find a diverse range of clothing items at Fashion Bandung. This includes shirts, T-shirts, trousers, jeans, shorts, jackets, suits, accessories, and more. The brand ensures that all products are designed to provide both comfort and style, with a perfect fit that enhances the wearer’s confidence.
With an emphasis on customer satisfaction, Fashion Bandung offers a seamless shopping experience. The brand’s physical store provides a welcoming and well-organized space, where customers can browse through the various clothing options at their own pace. Knowledgeable and friendly staff members are also available to assist customers and provide personalized style recommendations.
In addition to its brick-and-mortar store, Fashion Bandung also operates an online platform, allowing customers to conveniently shop for their favorite items from the comfort of their own homes. The brand offers secure online transactions and efficient delivery services, ensuring that customers receive their purchases in a timely manner.
Fashion Bandung strives to be more than just a clothing brand; it aims to be a source of inspiration and a fashion destination for men who appreciate style and quality. Whether you are looking to update your wardrobe with the latest trends or searching for a timeless piece that exudes elegance, Fashion Bandung has something for every man’s fashion needs.
See more:

